Experimental Physics
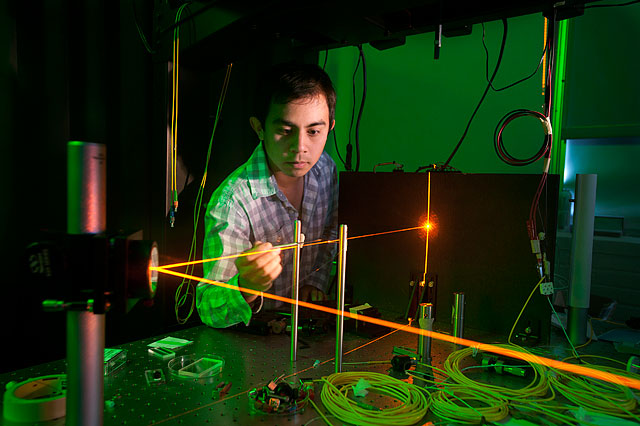
Students conducting research with our experimental physics faculty work in one of several laboratories hosted within the department. Our facilities host several million dollars' worth of equipment—including atomic force microscopes, plasma reactors, lasers, and optical benches—which trains students to work on experimental setups widely used in industry and post-graduate research. The research interests of our experimental physics faculty span a wide range of physics sub-fields, including optics, biophysics, plasma physics, and solid-state physics.
About the Faculty

Nina Abramzon
Professor
Professor Abramzon studies the effects of atmospheric pressure plasmas on surface modification. The applications of the surface treatment work studied in the our lab include biofilm growth prevention, enhancement of the binding of antibodies to glass surfaces, and reduction of bone cement failure. She uses optical emission spectroscopy to study different plasma characteristics, such as composition and temperature in order to understand the mechanisms beyond the plasma process. She collaborates on these projects with faculty from Biology, Physics and Material Science. Some of the instruments in the lab include three SURFX atmospheric pressure plasma reactors and various spectrometers including Optics spectrometers HR 4000 Ocean and an Acton SP2156 Spectrometer with PIXIS100 CCD detector.
Ertan Salik
Professor
Professor Salik specializes in the development of fiberoptic sensors, which can be used in physical, chemical, and biological detection. These sensors, referred to as single mode-multimode-single mode (SMS) fiber sensors in the literature, are highly sensitive to temperature and stress changes, making them ideal for structural health monitoring. Dr. Salik has also developed SMS sensors as biosensors capable of detecting proteins, viruses, and bacteria, with applications spanning medical diagnosis, food safety, environmental monitoring, and biodefense. Dr. Salik’s lab is an interdisciplinary one, hosting students from diverse fields such as Physics, Biology, Electrical Engineering, and Mechanical Engineering. The lab is equipped with an array of advanced instruments, including: multiple optics tables, numerous opto-mechanical and optical components, lasers, laser controllers, and optical spectrum analyzer (350-1700 nm), optical fiber components (couplers, amplifiers, polarization controllers, modulators, etc) , a 3D printer, oscilloscopes, function generators, a refrigerator/freezer, analytical balances, fume hood, microcentrifuge, hybridization oven.
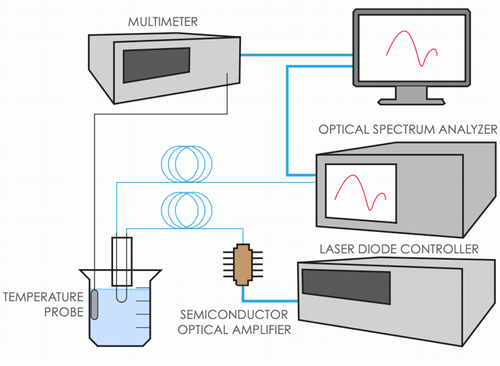

Krishna Sigdel
Assistant Professor
Professor Sigdel uses Atomic force microscopy to probe the biomolecules in single molecule level. He studies the structure and dynamics of membrane proteins in near native environment and at physiological condition. Dr. Sigdel is currently developing his lab and will be installing an atomic force microscope to study membrane proteins. His research is fully interdisciplinary where student from Physics, Engineering, Chemistry/Biochemistry, and Biology can work. Dr. Sigdel also collaborates with Dr. Arthur Roberts from College of Pharmacy, University of Georgia, Athens to study membrane protein-drug interaction and Prof. Steve White at University of California Irvine for membrane protein-lipid interaction studies
Kurt Vandervoort
Professor Emeritus
Professor Vandervoort has used both scanning tunneling and atomic force microscopes in a variety of investigations. His most recent work involves studying the surface of moth eyes at the sub-micron scale. These surfaces consist of hexagonal arrays of cone shaped bumps about 100 nm in height, that inhibit light reflection, thus enhancing light absorption. This field of study has attracted significant interest due to many potential applications, for example, in micropatterning thin films to enhance the efficiency of solar cells.
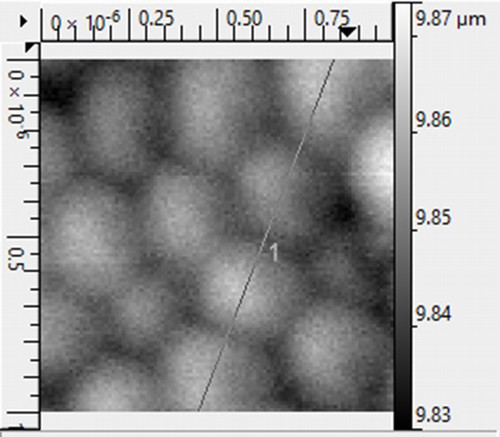
Olivia D Walsh, Leona Choi, and Krishna P. Sigdel, ‘’Effect of CM15 on supported lipid bilayer probed by atomic force microscopy’’ Membranes, 13, 864 (2023)
T. R. Matin, M. Utjesanovic, K.P. Sigdel, V. F. Smith, I. Kosztin, G. M. King; “Characterizing the locus of a peripheral membrane protein-lipid bilayer interaction underlying protein export activity in E. coli” Langmuir, 36, 2143-2152 (2020)
P. H. Nguyen, K. P. Sigdel, K. G. Shaefer, G.A.K. Mensah, G. M. King, A. G. Roberts; “The effects of anthracycline drugs on the conformational distribution of mouse P-glycoprotein explains their transportrate differences” Biochemical Pharmacology, 174, 113813 (2020)
M. Utjesanovic, T. R. Matin, K.P. Sigdel, G. M. King, I. Kosztin; “Multiple stochastic pathways in forced peptide-lipid membrane detachment” Scientific Reports, 9, 451 (2019)
K. P. Sigdel, L. A. Wilt, B.P. Marsh, A.G. Roberts, and G. M. King; “The conformation and dynamics of P-glycoprotein in a lipid bilayer investigated by atomic force microscopy” Biochemical Pharmacology, 156, 302 (2018)
Robert M. Nelson, Mark D. Boryta, Bruce W. Hapke, Kenneth S. Manatt, Yuriy Shkuratov, V. Psarev, Kurt Vandervoort, Desire Kroner, Adaze Nebedum, Christina L. Vides, John Quiñones. "Laboratory simulations of planetary surfaces: Understanding regolith physical properties from remote photopolarimetric observations." Icarus 302, 483-498 (2018)
Sigdel K.P., Pittman A.E., Matin T.R., King G.M. (2018) High-Resolution AFM-Based Force Spectroscopy. In: Lyubchenko Y. (eds) Nanoscale Imaging. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1814. Humana Press, New York, NY.
T. R. Matin, K.P. Sigdel, M. Utjesanovic, B. P. Marsh, F. Gallazzi, V. F. Smith, I. Kosztin and G. M. King, “Single-molecule peptide-lipid affinity assay reveals interplay between solution structure and partitioning” Langmuir, 33, 4057 (2017). DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b00100
J. Miller, A. Castaneda, K. H. Lee, M. Sanchez, A. Ortiz , E. Almaz , Z. T. Almaz , S. Murinda , W.-J. Lin and E. Salik, Biconically Tapered Fiber Optic Probes for Rapid Label-Free Immunoassays, (2015) Biosensors, 5(2), 158-171
K.P. Sigdel, J.S. Grayer, and G.M. King; “Three dimensional atomic force microscopy: Interaction force vector by direct observation of tip trajectory” Nano Letters, 13, 5106 (2013) DOI: 10.1021/nl403423p
K. Vandervoort and G. Brelles-Mariño, Cal Poly Pomona NUE Project: Implementing Microscale and Nanoscale Investigations Throughout the Undergraduate Curriculum. (2013) J. Nano Educ. 5, 51-60
E. Salik, M. Medrano, G. Cohoon, J. Miller, C. Boyter, J. Koh, “SMS fiber sensor utilizing a few-mode fiber exhibits critical wavelength behavior,” (2012) IEEE Photonics Technology Letters. DOI:10.1109/LPT.2012.2184090
E. Salik, “Quantitative investigation of Fresnel reflection coefficients by polarimetry,” (2012) American Journal of Physics, 80, 216. DOI: 10.1119/1.3672851
Z. Guo, C. Boyter, G. Cohoon, E. Salik, and W.-J. Lin, “Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin by a Tapered Fiber Optic Biosensor,” (2011) GSTF International Journal of Bioinformatics and Biotechnology, 1, 1.
Tseng S, Abramzon N, Jackson J. O., Lin W. “Gas discharge plasmas are effective in inactivating Bacillus and Clostridium spores” (2011) Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, DOI 10.1007/s00253-011-3661-0
G. Cohoon, C. Boyter, M. Errico, K. Vandervoort, and E. Salik, ”Enhancing sensitivity of tapered fiber optic sensors by multiple passes through the sensor,” (2010) SPIE Optical Engineering, Volume 49 (3) 034401
J. C. Joaquin, C. Kwan, N. Abramzon, K. Vandervoort, & G. Brelles-Marino, Is Gas-Discharge Plasma a New Solution to the Old Problem of Biofilm Inactivation? (2009) Microbiology, 155, 724
Vandervoort, K., Abramzon, N., & Brelles-Mariño, G. Plasma Interactions with Bacterial Biofilms as Visualized through Atomic Force Microscopy. (2008) IEEE Trans. on Plasma Science, 36, 1296
Abramzon N. & Siegel P.B. "Introductory Helium Atomic Spectrum Analysis" (2009) American Journal of Physics, 77, 920
Abramzon, N., Joaquin, J. C., Bray, J. D. & Brelles-Mariño, G. "Biofilm Destruction by RF High-Pressure Cold Plasma Jet." (2006) IEEE Trans. on Plasma Science, 34, 1304
K. G. Vandervoort, T. T. Nguyen, M. A. Demine, and W. K. Kwok, Measurements of the Meissner fraction as a function of oxygen ordering for oxygen deficient YBa2Cu3O7-d single crystals. (2006) Superconductor Science and Technology 19, 980
Becker, K., Koutsospyros, A., Yin, S. M., Christodoulatos, C., Abramzon, N., Joaquin, J. C. & Brelles-Mariño, G. 2005. Environmental and Biological Applications of Microplasmas. (2005) Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion, 47, B513